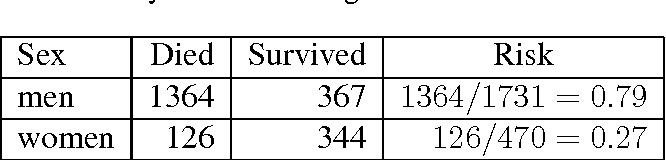
The conditional odds ratio assumes a full parametric structure, confidence intervals will be narrow –In general parametric assumptions are likely flawed –So not only will the conditional odds ratio always inflate the apparent magnitude of the association, but itSep 18, · Log odds and log hazard ratios have an unlimited ranges and can possibly apply to everyone This makes them good bases for studying heterogeneity of treatment effect When risk factors exist and a clinical trial enrolls patients having a variety of values of these risk factors, there will be outcome heterogeneityThis is called the odds ratio;
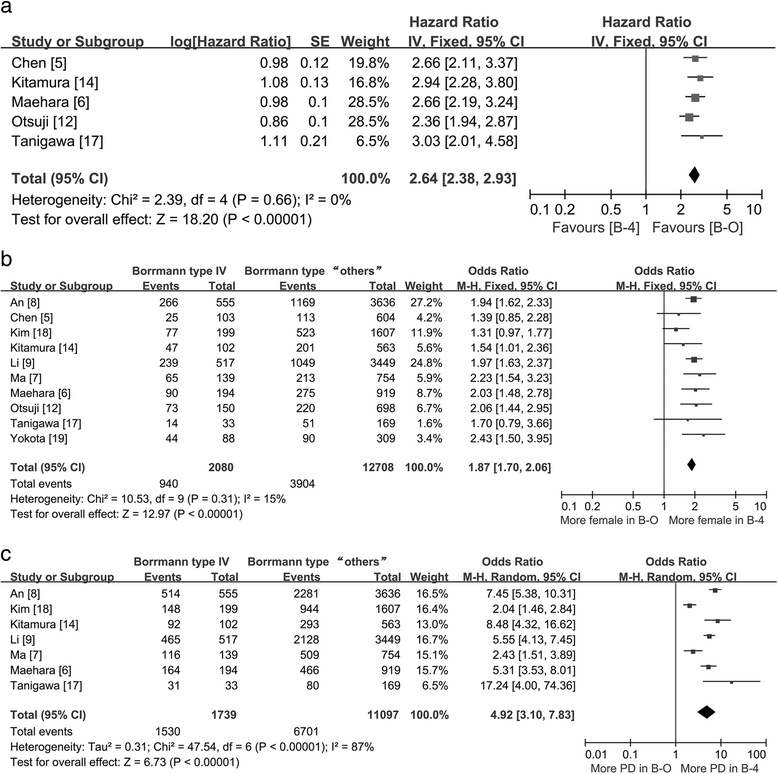
Clinicopathologic Characteristics And Prognosis Of Borrmann Type Iv Gastric Cancer A Meta Analysis World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text
Hazard ratio odds ratio unterschied
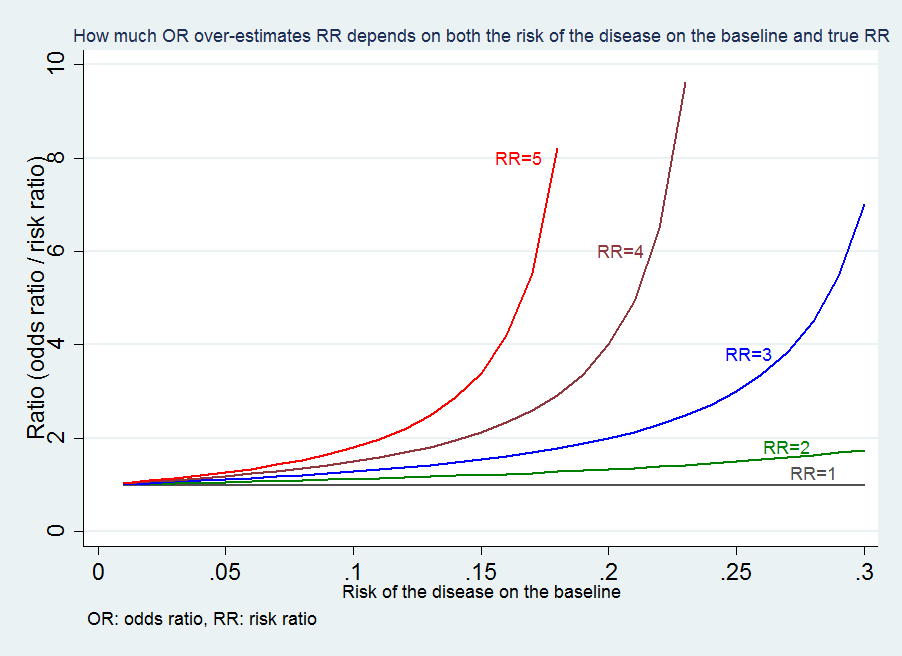
Hazard ratio odds ratio unterschied-Nov , 18 · To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrenceJul 01, 17 · After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in the study



Cetuximab And Chemotherapy As Initial Treatment For Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Nejm
Hazard ratio, odds, and probability of healing There is an alternative interpretation of the hazard ratio that may be intuitively easier to understand The hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher hazard reaches the endpoint first Thus, in a clinical trial examining time to disease resolution, itMay 04, 09 · Furthermore, the odds ratio of 258 for all persons is not a weighted average of the odds ratios of 265 for men and 291 for women, as 258 is closer to 1 than either stratumspecific estimate Adjusting the odds ratio of 258 for sex, using MantelHaenszel methods, produces an odds ratio of 279, though sex is not a confounderDec 08, 18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;
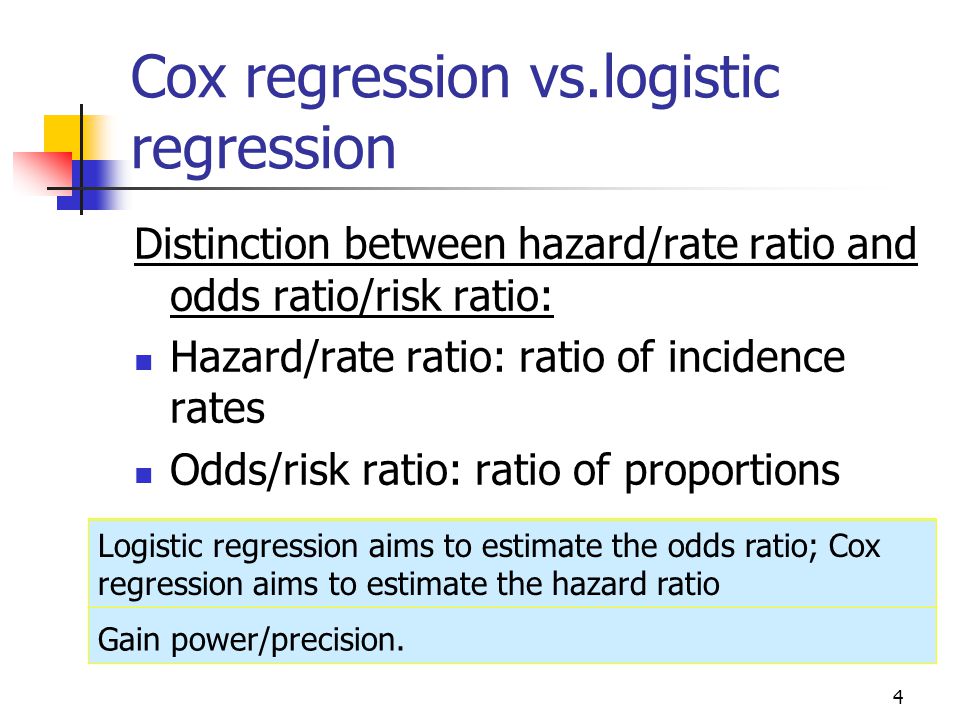
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalApr 05, 19 · The Hazard ratio (HR) is one of the measures that in clinical research are most often difficult to interpret for students and researchers In this post we will try to explain this measure in terms of its practical use You should know what the Hazard Ratio is, but we will repeat it1 Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between patients in clinics B and A who take 50mg dose of methadone 2 Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between two individuals who are at clinic A and whose dosage differs by 1 mg 3 Difference in log hazard ratio of dropout from the
Odds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatmentIt is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratiosAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators
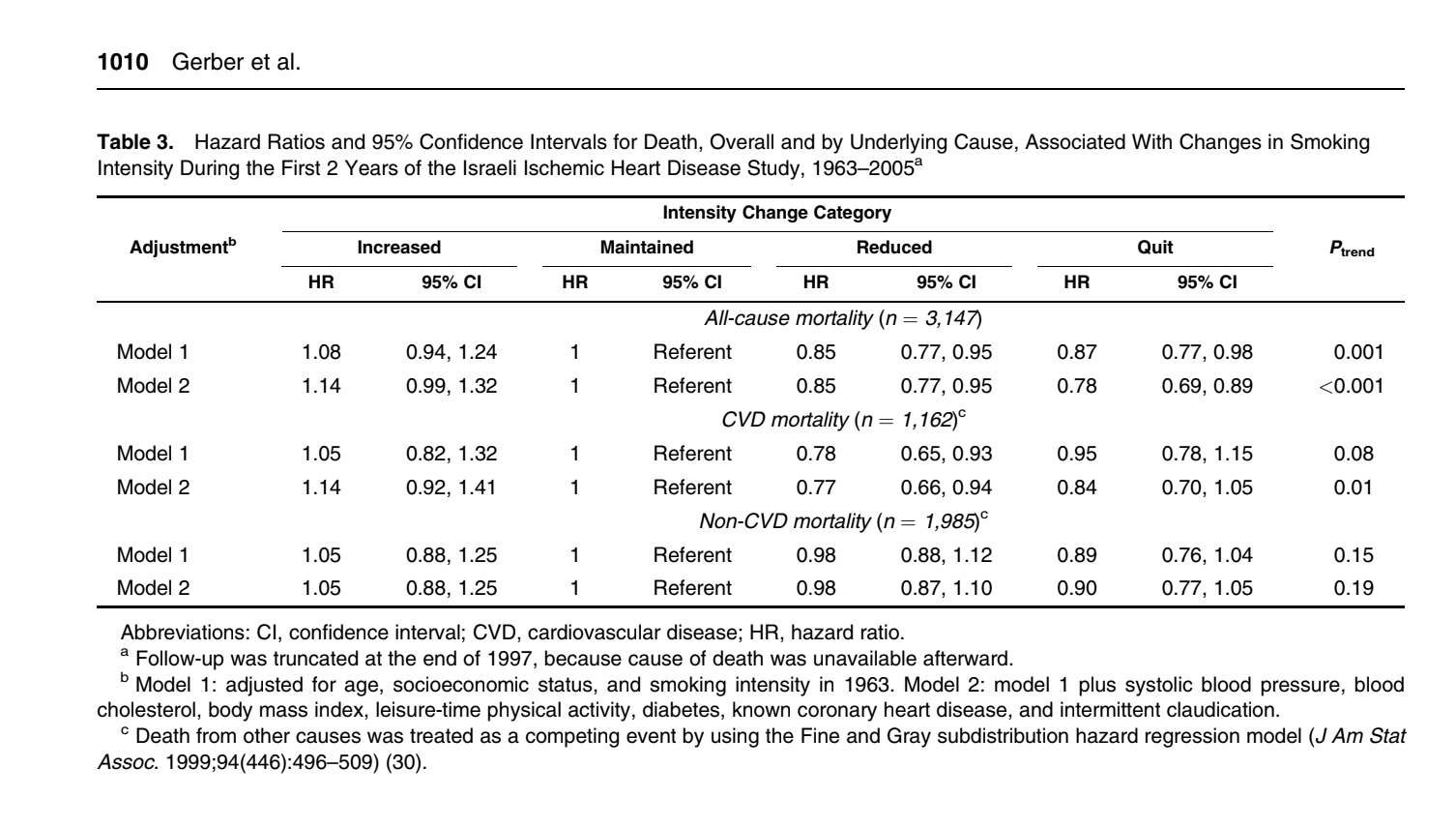


Solved Table 3 Provides Hazards Ratios 1 For The Reduce Chegg Com



Hazard Ratio Wikipedia
More on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (ie not symmetric) "protective" odds ratios range from 0 to 1 "increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men areMay 18, 12 · The odds ratio is the measure of choice in a casecontrol study (see Lesson 1) A casecontrol study is based on enrolling a group of persons with disease ("casepatients") and a comparable group without disease ("controls") The number of persons in the control group is usually decided by the investigatorThe method of presenting the results of clinical studies can
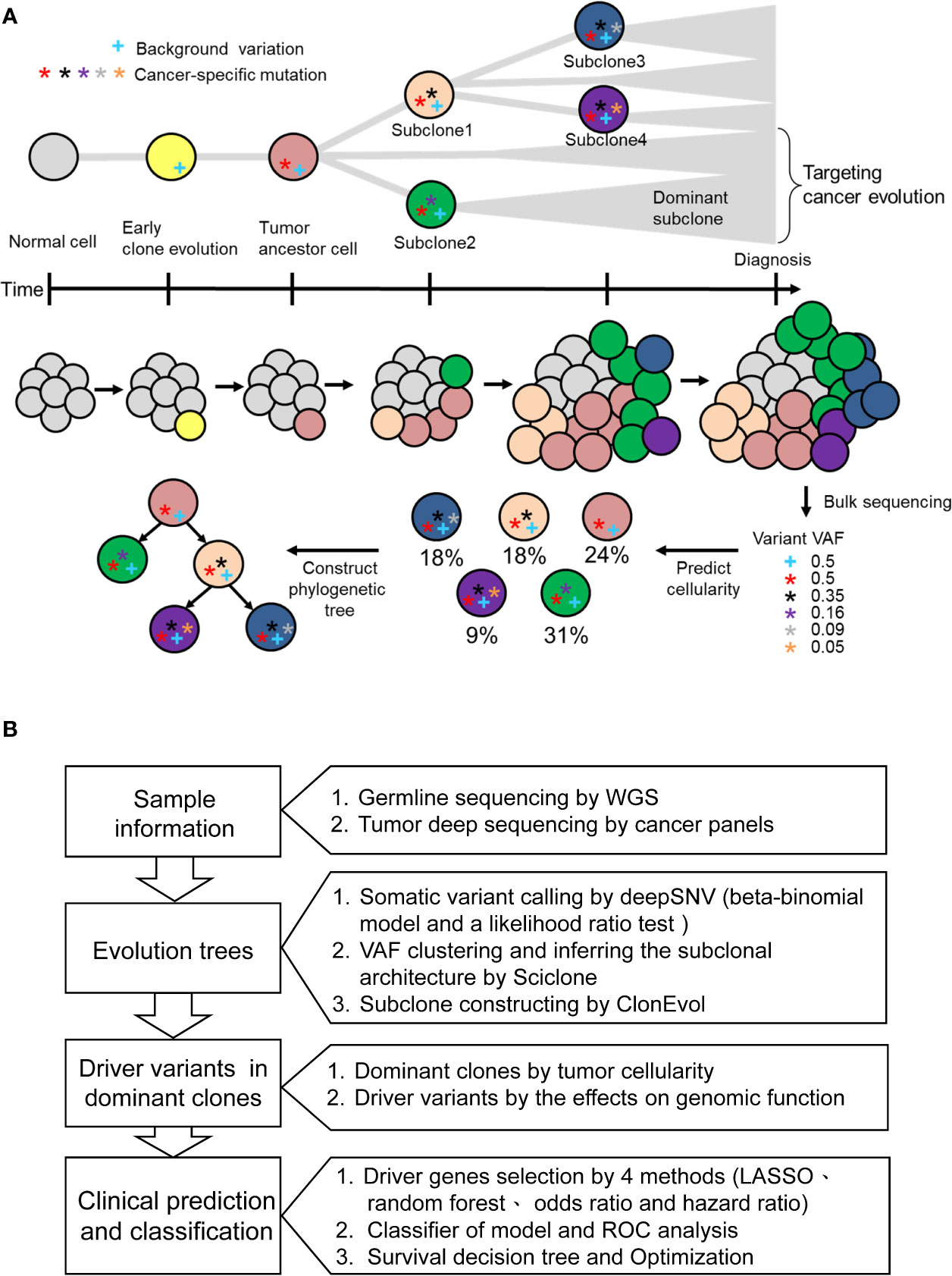


Frontiers Intratumor Heterogeneity Of Myo18a And Fbxw7 Variants Impact The Clinical Outcome Of Stage Iii Colorectal Cancer Oncology



The Utility Of Mortality Hazard Rates In Population Analyses Biorxiv
Hazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?Useful when the risk is not constant with respect to time It uses information collected at different times TheAug 13, 13 · The interpretation of a hazard ratio is essentially the same as an odds ratio However it's probably worth noting that whilst an odds ratio is derived from calculating the odds of an event in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratio



Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio For Complications Download Table
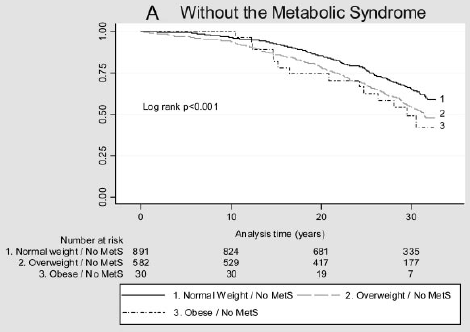


Lesson 13 Proportional Hazards Regression Stat 507
Aug 26, · Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while aMay 14, 19 · Le Hazard Ratio (HR) est proche du RR avec une dimension temporelle supplémentaire En effet, dès lors que l'on est en présence de données censurées, c'estàdire des temps d'événement inconnus à causes de durées de suivi différentes selon les patients, le tableau de contingence précédent n'est plus valableHazard and hazardratios Cumulative hazard at a time t is the risk of dying between time 0 and time t, and the survivor function at time t is the probability of surviving to time t (see also KaplanMeier estimates)



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
Jan , 21 · Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio 2101 Trending Your Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio pic are accessible in this web Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio are a theme that is being searched for and appreciated by netizens nowAn odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined It is undefined if p 2 q 1 equals zero, ie, if p 2 equals zero or qA razão de chances ou razão de possibilidades (em inglês odds ratio;



Odd Ratio Relative Risk Odds Ratio



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
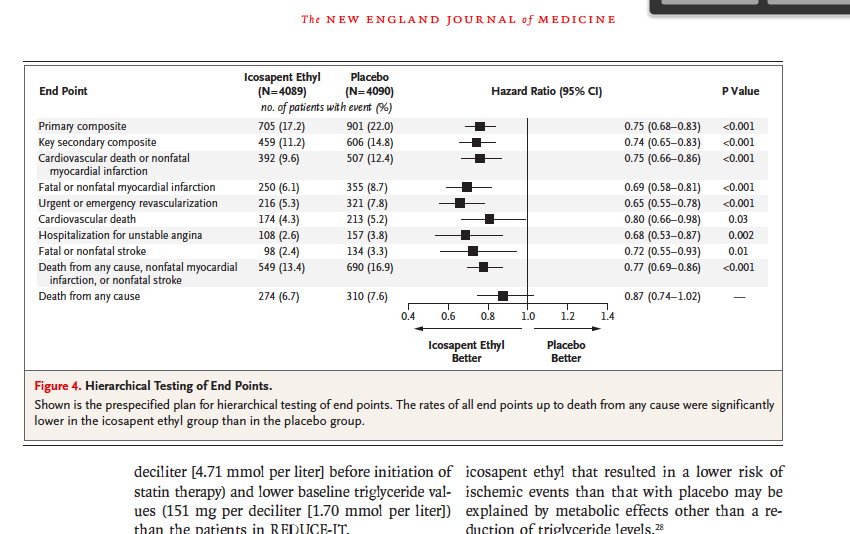
Aug 28, 15 · The initial results of the trial were reported after participants had been followed for a maximum of 500 days (median 57 months) During followup, mortality was significantly lower in the isoniazid group than in the placebo group (8% (n=11) v 16% (n=21);Jun 03, 16 · The hazard ratio is the ratio of these two expected hazards h 0 (t)exp (b 1a)/ h 0 (t)exp (b 1b) = exp(b 1(ab)) which does not depend on time, t Thus the hazard is proportional over time Sometimes the model is expressed differently, relating the relative hazard, which is the ratio of the hazard at time t to the baseline hazard, to the riskFeb 17, 21 · So, keep in mind that whenever we talk about the hazard ratio, relative risk, and odds ratio, there will always be a comparison to be made These values are dependent on another value for context Photo by Tingey Injury Law Firm on Relative risks all have a



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
Feb 01, 08 · In every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trials Table 3 Hazard ratio and timetoevent analysis 13) The Odds Ratio 4) After calculating the odds ratio, we observe a 3fold difference in the prevalence rate (75% vs 25%) change to a 9fold difference in the odds ratio Clearly, the two methods produce opposing results Effect of Changing Incidence on OR Problem Let us consider the relationship between smoking and lung cancerJun 07, 07 · Odds ratios (ORs) or relative risks (RRs) that measure only the number of events and take no account of when they occur are appropriate for measuring dichotomous outcomes, but less appropriate for analysing timetoevent outcomes Using such dichotomous measures in a metaanalysis of timetoevent outcomes can pose additional problems



Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table


Coefplot Plotting Regression Coefficients And Other Estimates In Stata
Hazard ratio 046, 95% confidence interval 022 to 095)Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) In casecontrol studies, andAbreviatura OR) é definida como a razão entre a chance de um evento ocorrer em um grupo e a chance de ocorrer em outro grupo Chance ou possibilidade é a probabilidade de ocorrência deste evento dividida pela probabilidade da não ocorrência do mesmo evento Esses grupos podem ser, por exemplo,



Clinical Trials In Hours Point Estimation Odds
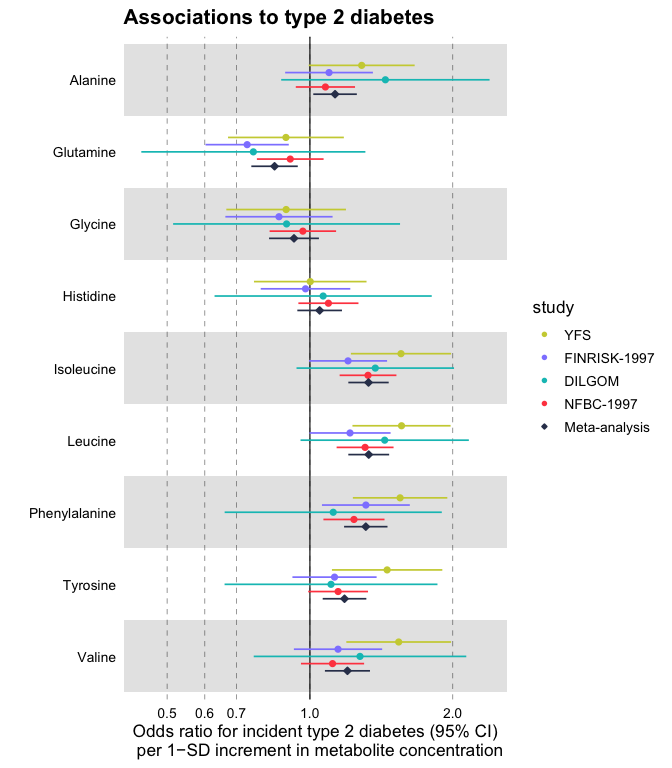


Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot
The hazard ratio is simply the value of the hazard calculated from the treatment curve, divided by the hazard calculated from the control curve Based on the complexity, statistical software is required to make this calculation to estimate the hazard ratio Figure 1 The timetoevent curve or KaplinMeier curveOdds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 03 67 66 Hazard ratio (HR) Broadly equivalent to relative risk (RR);Hazard ratio vs relative risk How to explain the difference between hazard ratio and In survival analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) is the ratio of the hazard rates corresponding to the conditions described by two levels of an explanatory variable For example, in a drug study, the treated population may die at twice the rate per uni



New Resource Can Help You Assess Hazards And Risks And Odds Ratios Laptrinhx News



Kaplanmeier Methods And Parametric Regression Methods Kristin Sainani
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notJul 11, 16 · It's a ratio of events to nonevents You can switch back and forth between probability and odds—both give you the same information, just on different scales If O1 is the odds of event in the Treatment group and O2 is the odds of event in the control group then the odds ratioIn logistic regression, an odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictor Are these not practically the same thing?


Coefplot Plotting Regression Coefficients And Other Estimates In Stata



Comparison Of Tenofovir Versus Entecavir On Reducing Incidence Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Gu Journal Of Gastroenterology And Hepatology Wiley Online Library
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsVariable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) groupIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;
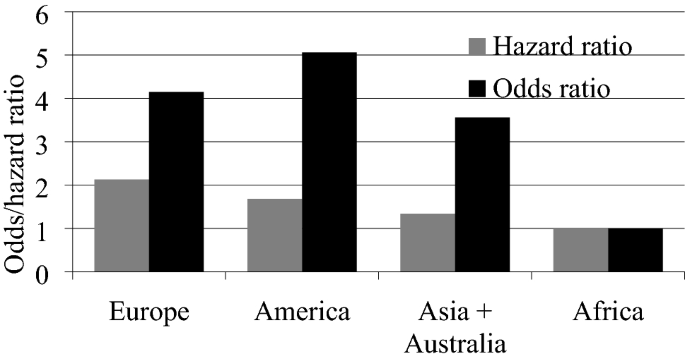


A Survival Analysis In The Assessment Of The Influence Of The Sars Cov 2 Pandemic On The Probability And Intensity Of Decline In The Value Of Stock Indices Springerlink



How To Rotate The Legend Labels To Match The Orientation In The Plot Stack Overflow
Jan 11, 18 · In this study Odds ratio is 93 which shows that the odds of having exposed to hormone replecement therapy is 9 times higher for cases compared to controls Odds ratios are not straight forward like percentage or relative risk but it has close approximation to them9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effectsJun 01, 11 · Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Please note that results shown are rounded to 2 decimal places, but the calculations used the raw numbers from the previous column ( c ) and therefore give different results than if the rounded numbers were used (eg, 006/008 = 075)



Highly Customized Analytical Graphs
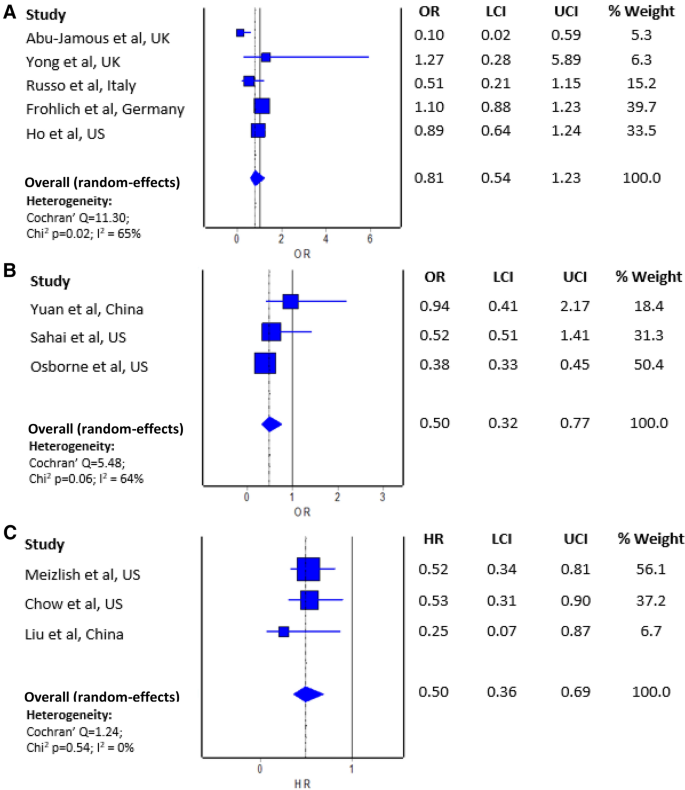


Use Of Antiplatelet Drugs And The Risk Of Mortality In Patients With Covid 19 A Meta Analysis Springerlink
Apr 05, 16 · Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RRThe hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereofIntervals and statistical vs clinical significance This second article will discuss absolute and relative risks, number needed to treat and harm, KaplanMeier survival curves and understanding diagnostic tests What are absolute risks, relative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
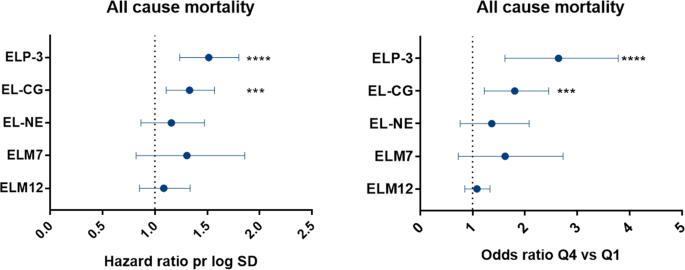


Specific Elastin Degradation Products Are Associated With Poor Outcome In The Eclipse Copd Cohort Scientific Reports


Drmeta


Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Difference
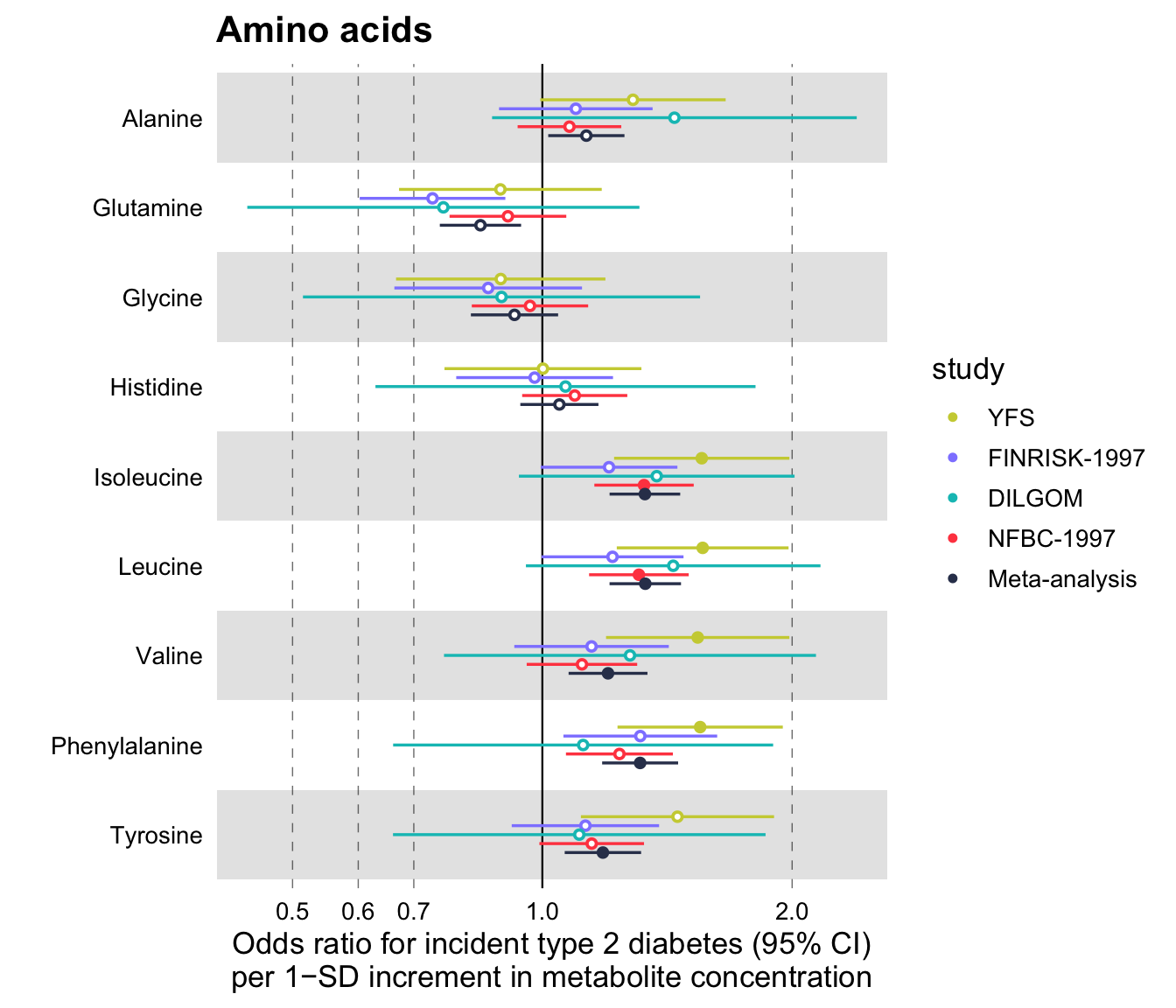


Using Ggforestplot Ggforestplot



Study Mortality With Hazard Rates Not Probabilities Biorxiv



Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table


Statistics 262 Intermediate Biostatistics Ppt Video Online Download



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Data Analysis Of Epidemiological Studies 19 03 10



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



Estimating The Relative Hazard By The Ratio Of Logarithms Of Event Free Proportions Sciencedirect


2 Which Of The Following Is Not A Measure Of Relative Risk A B C D E Odds Ratio Risk Ratio Hazard Ratio Number Needed To Treat Rate Ratio Course Hero



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
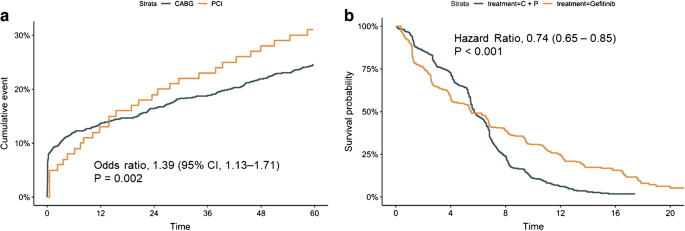


Model Free Estimates That Complement Information Obtained From The Hazard Ratio Springerlink



Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id



Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv



Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Increase In Hospital Download Scientific Diagram



Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Uberlebenszeitanalyse



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Lincom Stata


Cox Proportional Hazards Model Easy Guides Wiki Sthda



Clinicopathologic Characteristics And Prognosis Of Borrmann Type Iv Gastric Cancer A Meta Analysis World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text



Risk Factors For Suicidal Thoughts And Behaviors A Meta Analysis Of 50 Years Of Research



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Outcomes Shown For A Odds Ratio Analysis And B Hazard Ratio Download Scientific Diagram



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence


Solved State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Rr Chegg Com



Significant Improvement In Short And Long Term Kidney Transplant Survival Despite Stagnant Rates Of Delayed Graft Function Atc Abstracts


Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples Of Rr And Or For Different Probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 Rr Or 4 1 4 6 2 3 67 58 04 Pdf Document


Hazard Ratio Vs Relative Risk



Introduction To Cox Regression Kristin Sainani Ph D



Ctspedia Ctspedia Clinaegraph001



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad


Plos One Impact Of Geographic Origin On Access To Therapy And Therapy Outcomes In The Swiss Hepatitis C Cohort Study



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio Et Risque Relatif Quelles Differences



Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population



Related Image Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Odds


Graphpad Prism 9 User Guide Forest Plots


Plos One Influence Of Clinicopathological Characteristics And Comprehensive Treatment Models On The Prognosis Of Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Cervix A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis



Hazard Ratio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Hazard And Odds Ratios Image Eurekalert Science News



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Stat D Si Relative Risk Pdf4pro



Design And Analysis Of Clinical Study Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Dr Tuan V Nguyen Garvan Institute Of Medical Research Sydney Australia Ppt Download
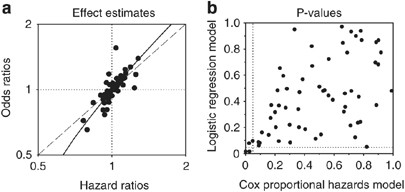


Cox Proportional Hazards Models Have More Statistical Power Than Logistic Regression Models In Cross Sectional Genetic Association Studies European Journal Of Human Genetics



Cetuximab And Chemotherapy As Initial Treatment For Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Nejm



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
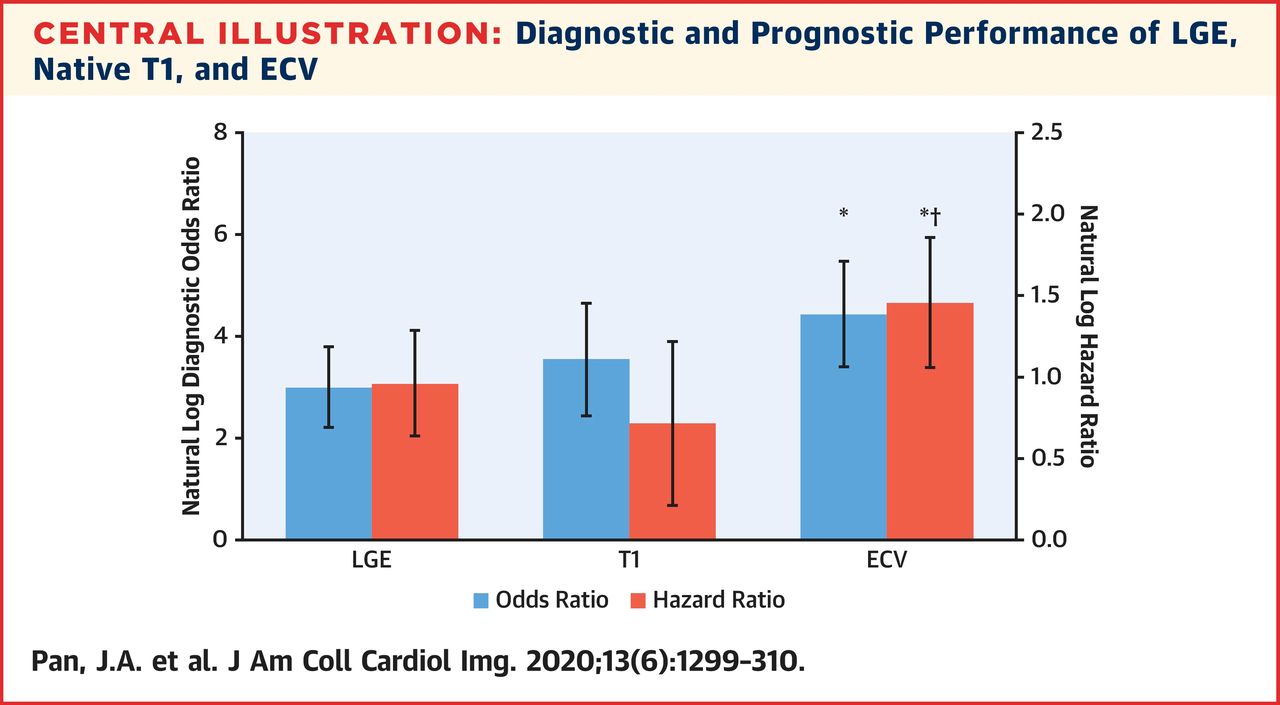


Jacc Journals Jaccimg Explores Cmr In Cardiac Amyloidosis T1 Mapping Has Similar Sensitivity Specificity While Avoiding Contrast Ecv Has Highest Diagnostic Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio For Adverse Events



Various Estimates For The Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Of Herpes Download Table



Thread By Profdfrancis Risk Ratio Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio 2nd And Final Part Of The Tweetorial From Orbita Hq Fun Easy And Informativ Meded Foamed Cardiology Cardiotwitter



Odds Ratios Index Hospitalization And Hazard Ratio Follow Up Period Download Table



Math3010 Week 6



Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table
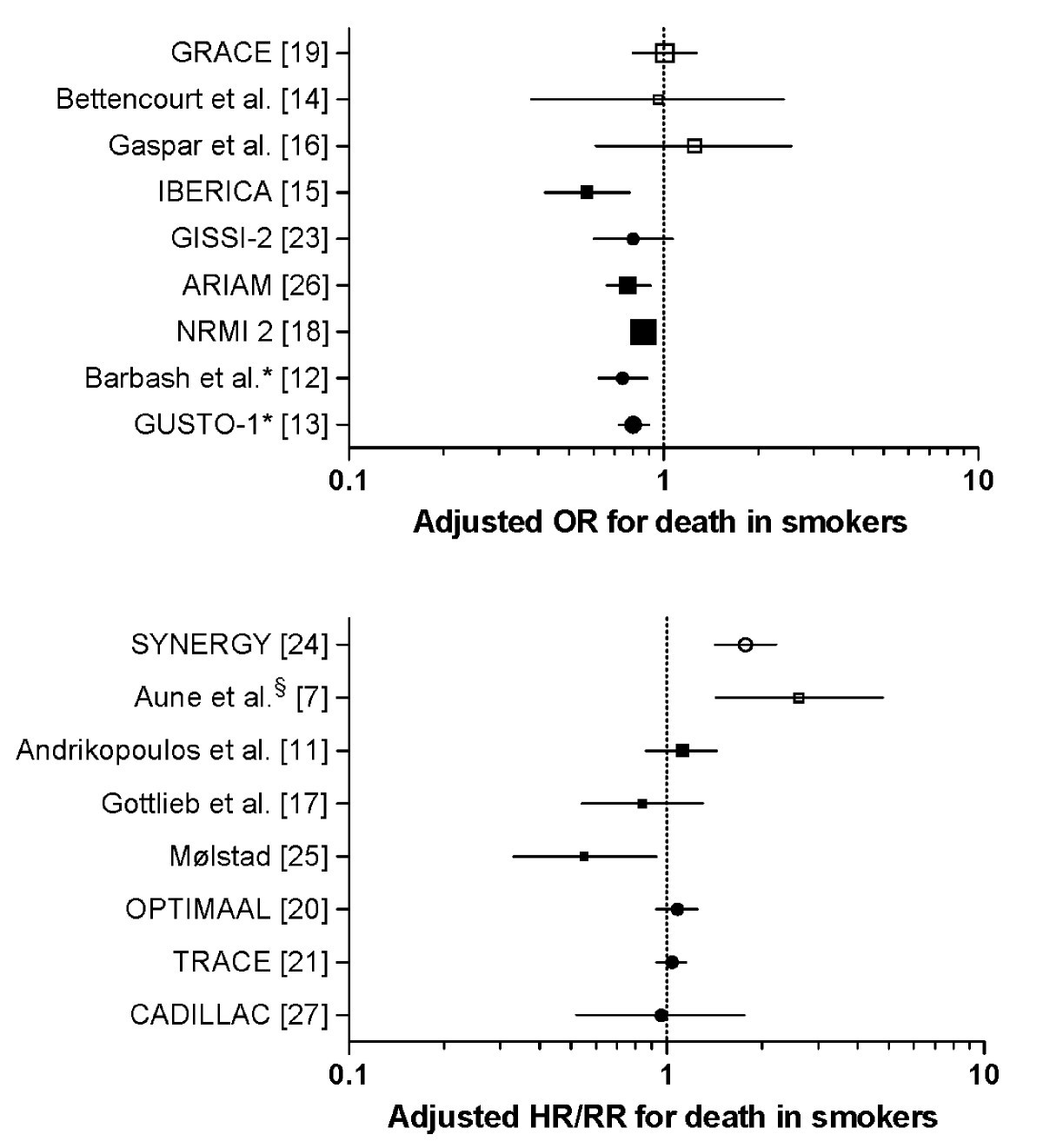


The Smoker S Paradox In Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome A Systematic Review Bmc Medicine Full Text
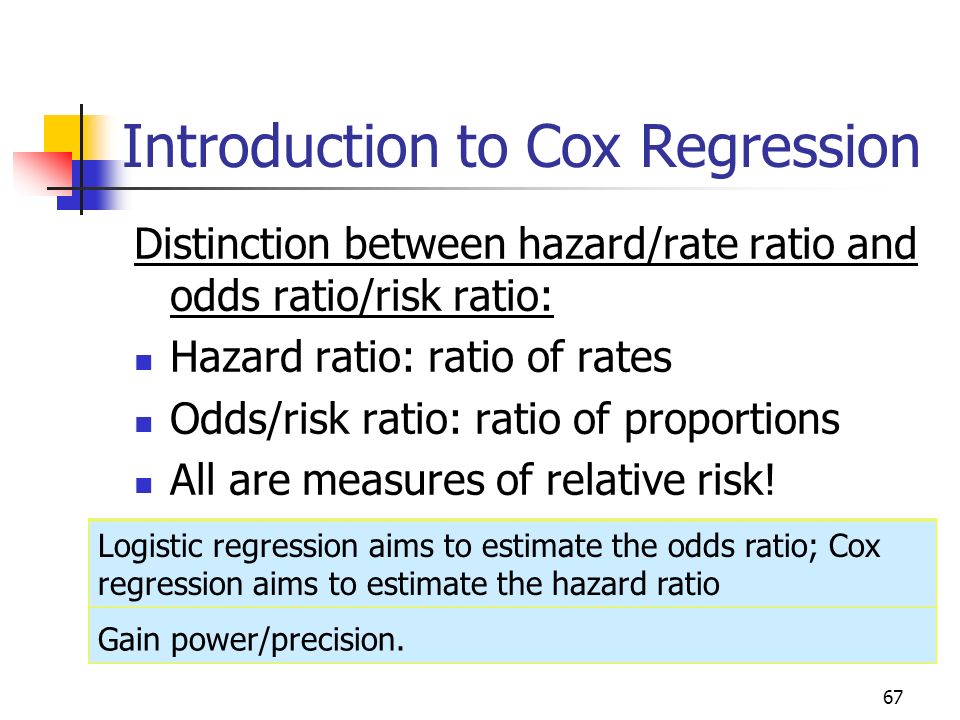


Tests For Time To Event Outcomes Survival Analysis Ppt Download


Plos One Delirium As A Predictor Of Mortality And Disability Among Hospitalized Patients In Zambia
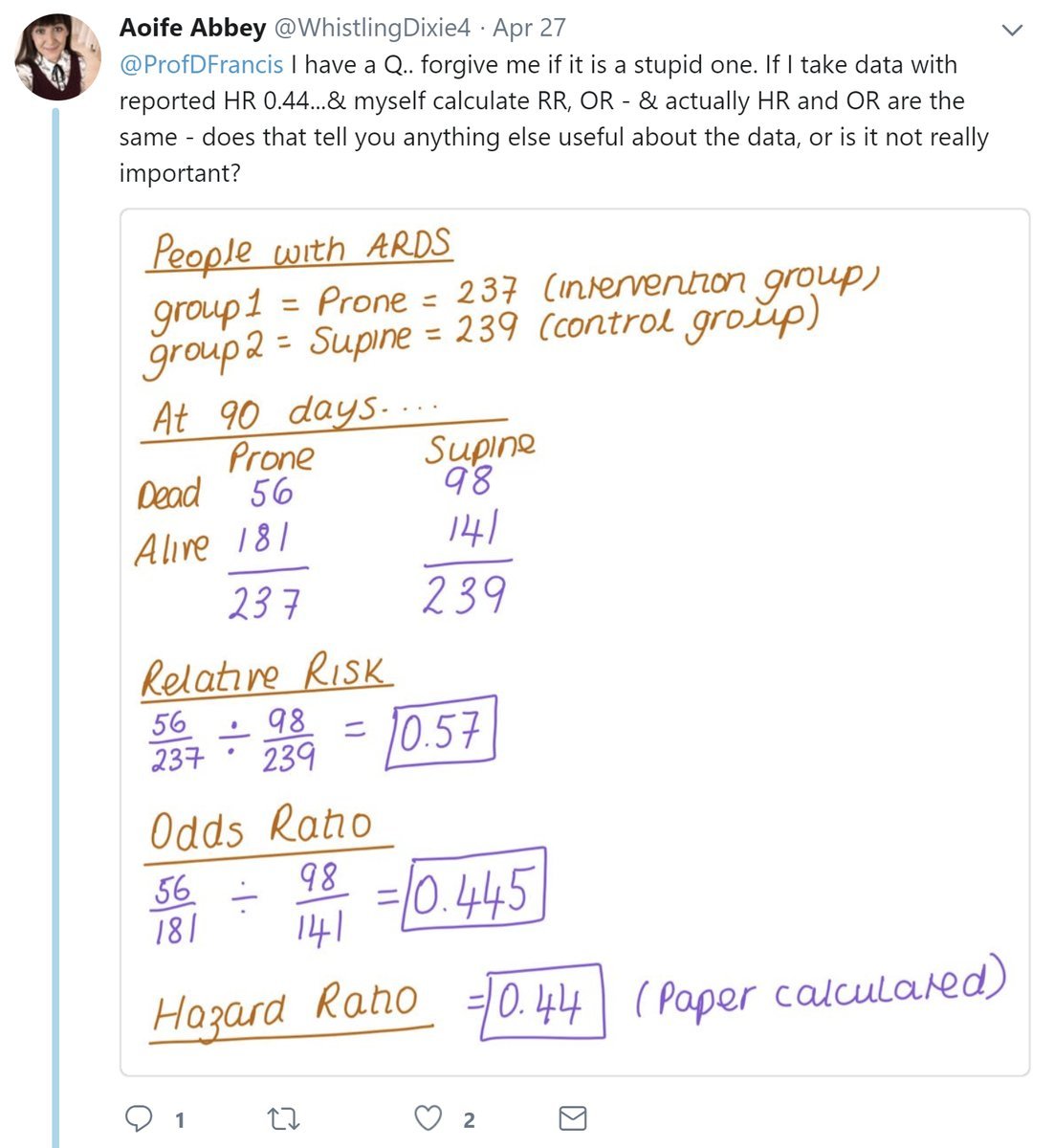


Prof Darrel Francis Mk Cardiofellows Great Again The Hazard Ratio Is In A Way The Best Thing We Could Calculate Because It Looks Along Every Instant In Time And



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv


Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies


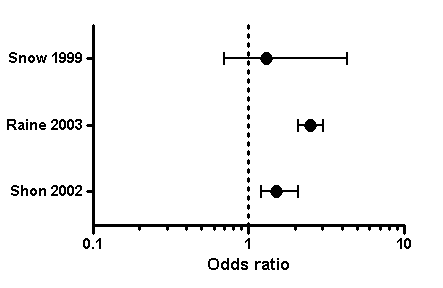
How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk
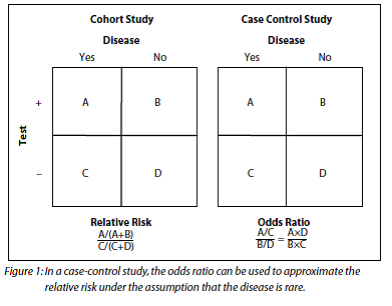


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿